Sore Breasts and Ovulation: Your Guide to Causes, Symptoms & Relief

Key points
- Estrogen's Role: In the first half of your cycle (the follicular phase), estrogen levels rise to prepare for ovulation. Estrogen stimulates the growth and enlargement of the milk ducts within your breasts.
- Progesterone's Impact: After an egg is released during ovulation, your body enters the luteal phase. Progesterone levels rise significantly to prepare the uterine lining for a potential pregnancy. This hormone causes the milk glands (lobules) in the breasts to swell and can lead to increased tenderness, fullness, and pain.
Experiencing sore, tender, or swollen breasts around the middle of your menstrual cycle is a common, and often confusing, symptom. This discomfort, medically known as cyclical mastalgia, is frequently linked to ovulation. While it's usually a normal part of the monthly hormonal rhythm, it can raise questions about fertility, pregnancy, and overall breast health.
This comprehensive guide synthesizes medical insights and research to explain why your breasts hurt during ovulation, how to distinguish this symptom from others, and what you can do for relief.
Why Do Breasts Hurt During Ovulation? The Hormonal Connection
The primary reason for breast soreness around ovulation is the fluctuation of key reproductive hormones. Your menstrual cycle orchestrates a complex hormonal dance, and your breast tissue is highly responsive to these changes.
- Estrogen's Role: In the first half of your cycle (the follicular phase), estrogen levels rise to prepare for ovulation. Estrogen stimulates the growth and enlargement of the milk ducts within your breasts.
- Progesterone's Impact: After an egg is released during ovulation, your body enters the luteal phase. Progesterone levels rise significantly to prepare the uterine lining for a potential pregnancy. This hormone causes the milk glands (lobules) in the breasts to swell and can lead to increased tenderness, fullness, and pain.
This hormonal combination creates the perfect conditions for the dull, achy soreness many experience. According to research from Johns Hopkins Medicine, this type of cyclical pain is the most common form of breast discomfort and is nearly always hormonal [[3]].
Interestingly, a study from the University of British Columbia found that mild breast tenderness and swelling are more common in cycles with normal ovulation than in those with ovulatory disturbances, suggesting it can be a sign of a healthy, functioning cycle [news source 1].
 Breast tenderness often peaks during the luteal phase, after ovulation, due to a rise in progesterone. Source: Tuune Blog
Breast tenderness often peaks during the luteal phase, after ovulation, due to a rise in progesterone. Source: Tuune Blog
What Does Ovulation Breast Soreness Feel Like?
The sensation of ovulation-related breast pain can vary from person to person and even from cycle to cycle. Common descriptions include:
- A dull, heavy, or aching pain.
- General tenderness to the touch.
- A feeling of fullness or swelling.
- Increased sensitivity, especially in the nipples.
- Pain that affects both breasts, often in the upper, outer quadrants.
- Discomfort that can sometimes radiate into the underarm area.
The pain typically begins around the time of ovulation and lasts through the luteal phase, usually subsiding when your period starts and hormone levels drop.
Ovulation vs. PMS vs. Early Pregnancy: How to Tell the Difference
Because hormonal shifts are responsible for breast soreness in multiple scenarios, it can be difficult to pinpoint the cause based on this symptom alone. However, subtle differences in timing and accompanying symptoms can offer clues.
| Symptom Feature | Ovulation / PMS Soreness | Early Pregnancy Soreness |
|---|---|---|
| Timing | Starts mid-cycle (ovulation) or 1-2 weeks before your period (PMS). It resolves when or shortly after your period begins. | Starts around the time of a missed period or slightly before. It persists and may intensify instead of disappearing. |
| Sensation | Often a dull, heavy ache. Breast tissue may feel dense or "lumpy." | Frequently described as more intense, tingly, or sensitive. Breasts may feel fuller and heavier. |
| Other Symptoms | Accompanied by typical PMS symptoms like bloating, mood swings, food cravings, and headaches. | May be accompanied by a missed period, light spotting (implantation bleeding), nausea, fatigue, and darkening of the areolas. |
The most reliable way to determine if you are pregnant is to take a home pregnancy test after a missed period.
Is Breast Soreness a Reliable Way to Track Ovulation?
While breast tenderness is linked to the hormonal events following ovulation, it is not considered a reliable method for tracking your fertile window. The American Pregnancy Association lists it as a secondary, less common symptom of ovulation [2].
The main reasons it's unreliable are:
- Timing: The pain typically starts after ovulation has already occurred, meaning you have already passed your most fertile days.
- Subjectivity: The experience and intensity of the pain are highly individual and can change from month to month.
- Overlap: The symptom is too similar to PMS and early pregnancy signs to be a definitive indicator of ovulation.
More Accurate Fertility Tracking Methods
For those trying to conceive, relying on primary fertility signs is far more effective:
- Ovulation Predictor Kits (OPKs): These tests detect the surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) that triggers ovulation.
- Basal Body Temperature (BBT) Charting: Tracking your temperature first thing in the morning can confirm that ovulation has occurred.
- Cervical Mucus Monitoring: Observing changes in your cervical mucus throughout your cycle can help identify your most fertile days.
 While breast soreness is a common symptom, more reliable methods like ovulation tests and temperature charting are recommended for accurate fertility tracking. Source: Mother & Baby
While breast soreness is a common symptom, more reliable methods like ovulation tests and temperature charting are recommended for accurate fertility tracking. Source: Mother & Baby
How to Manage and Relieve Ovulation Breast Pain
For many, cyclical breast pain is a manageable annoyance. If you're looking for relief, several lifestyle adjustments and home remedies can help.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Wear a Supportive Bra: A well-fitting bra can significantly reduce discomfort by minimizing movement. Consider a supportive sports bra for exercise or even for sleeping if the pain is severe.
- Apply Warm Compresses: A warm cloth or heating pad applied to the breasts can soothe aches and pains.
- Adjust Your Diet: Some evidence suggests that reducing intake of caffeine, salt, and high-fat foods in the two weeks before your period may lessen symptoms for some women.
- Consider Supplements: Some studies suggest that supplements like Vitamin E and magnesium may help, but you should always consult your doctor before starting any new supplement regimen.
Medical Options
If the pain is severe and interferes with your daily life, over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications like ibuprofen can provide relief. For persistent and debilitating cases, a doctor may discuss hormonal treatments, such as oral contraceptives, which can help regulate the hormonal fluctuations that cause the pain.
 Lifestyle adjustments and self-care can help manage cyclical breast discomfort. Source: Kiindred
Lifestyle adjustments and self-care can help manage cyclical breast discomfort. Source: Kiindred
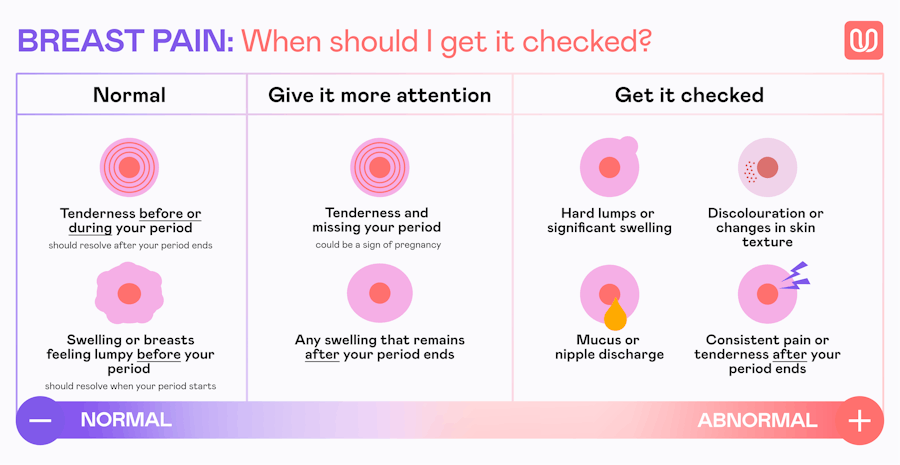
When to See a Doctor: Understanding 'Normal' vs. Atypical Symptoms
It's important to remember that cyclical breast pain is extremely common and rarely a sign of breast cancer. However, you should always consult a healthcare provider if you experience symptoms that deviate from the typical cyclical pattern.
Seek medical advice if you notice:
- A new or changing lump in your breast or underarm.
- Pain that is severe, persistent, or not related to your menstrual cycle (non-cyclical pain).
- Pain localized to one specific spot rather than a general ache.
- Skin changes on the breast, such as redness, dimpling, puckering, or an orange-peel texture.
- Nipple changes, such as an inverted nipple or unusual discharge (especially if it's bloody, clear, or from only one breast).
- Signs of infection, like redness, warmth, and fever.
A healthcare professional can provide a proper evaluation and peace of mind. While cyclical soreness is a normal part of life for many, you should never hesitate to get checked if something feels wrong.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How many days does breast tenderness from ovulation last? A: Breast tenderness linked to ovulation can vary, but it typically starts a few days before ovulation and continues until your period begins. For many, the discomfort subsides or disappears once menstruation starts. Tracking your symptoms can help you identify your personal pattern.
Q: Can only one breast hurt during ovulation? A: Yes, it is completely normal for cyclical breast pain to be more pronounced in one breast than the other. Hormonal changes affect your entire body, but the response in your breast tissue may not be perfectly symmetrical.
Q: Do breasts get bigger or swell during ovulation? A: Yes, some women experience noticeable breast swelling, fullness, or a feeling of heaviness around ovulation and in the days leading up to their period. This is caused by hormonal changes that lead to the growth of milk glands and increased blood flow to the area.
Q: Is it normal for nipple soreness to be the main symptom? A: Yes, for some individuals, the sensitivity is concentrated in the nipples rather than the entire breast. Sore, achy, or sensitive nipples are a common variation of cyclical breast pain and are caused by the same hormonal shifts.
References
- Villines, Z. (2020). Sore nipples: Ovulation, pregnancy, or another cause? Medical News Today. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/sore-nipples-ovulation
- Mira Fertility. (2025). Do Breasts Hurt During Ovulation? (What to Expect when TTC). https://shop.miracare.com/blogs/resources/breasts-hurt-ovulation
- Johns Hopkins Medicine. Breast Pain (Mastalgia). https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/mastalgia-breast-pain
- Clearblue. (2024). Five common ovulation questions and answers. https://www.clearblue.com/menstrual-cycle/5-common-ovulation-health-questions
- Health.com. (2025). Breast Changes 101: What To Expect During the Menstrual Cycle. https://www.health.com/condition/menstruation/breast-changes-during-menstrual-cycle
- [News Source 1] Contemporary OB/GYN. (2025). Breast tenderness and swelling found in normal ovulation. https://www.contemporaryobgyn.net/view/breast-tenderness-and-swelling-found-in-normal-ovulation

About the author
Sofia Rossi, MD, is a board-certified obstetrician-gynecologist with over 15 years of experience in high-risk pregnancies and reproductive health. She is a clinical professor at a top New York medical school and an attending physician at a university hospital.